Table of Contents
Second-Level Domain (SLD)
A Second-Level Domain (SLD) is an essential part of a website’s domain name structure. It sits directly to the left of the Top-Level Domain (TLD), which is the suffix like .com, .org, or .net.
For example, in the domain example.com:
- SLD:
example - TLD:
.com
The SLD is the unique, customizable part of a domain name that identifies the specific website or organization. In most cases, it represents the brand name, business, or an individual’s chosen identifier, making it a critical element for online identity and branding.
Role of the SLD in DNS Resolution
- When a user enters a domain name (e.g.,
example.com) in a browser, the DNS system translates it into an IP address through a series of queries. - The query begins at the root server and moves through the TLD nameservers (for
.com) and then to the SLD nameservers (forexample.com). - The SLD level directs the query to specific resources, such as web servers or email servers, which provide the content or service requested by the user.
Structure of a Domain Name
In a typical domain name setup like www.example.com:
- Third-Level Domain (or Subdomain):
www(often optional or customizable) - Second-Level Domain (SLD):
example(the unique portion chosen by the domain owner) - Top-Level Domain (TLD):
.com(defines the broader category or type of domain)
Why SLDs Matter
- Brand Recognition: The SLD often reflects the brand name, making it a crucial part of a website’s identity.
- SEO & Memorability: A clear, relevant SLD can make the domain easier for users to remember, improving direct traffic and SEO.
- Uniqueness: Since domain names need to be unique, the SLD provides a unique identifier when combined with a TLD, differentiating one website from another.
In short, the SLD is a foundational part of web addresses, shaping a site’s identity and making it easily accessible and recognizable online.
Difference between Second-Level Domain (SLD) and Top-Level Domain (TLD)
The Second-Level Domain (SLD) and Top-Level Domain (TLD) are both parts of a website’s domain name, but they serve different purposes and occupy different positions in the domain hierarchy. Here’s a breakdown of each and how they differ:
1. Position in the Domain Structure
- SLD (Second-Level Domain): The SLD is the part of the domain name that comes immediately before the TLD. It’s the portion that is often unique to a brand, business, or organization. For example, in
example.com, the SLD isexample. - TLD (Top-Level Domain): The TLD is the part of the domain name that follows the SLD, often known as the domain “extension.” Common TLDs include
.com,.org, and.net. For example, inexample.com, the TLD is.com.
2. Purpose and Meaning
- SLD: The SLD typically reflects the name, brand, or focus of the website. It helps users identify the organization or individual behind the website, making it a key part of the site’s identity.
- TLD: The TLD generally indicates the category, purpose, or geographical area of the domain. For example:
.comis traditionally used for commercial businesses..orgis often used by non-profit organizations..eduis reserved for educational institutions.- Country-code TLDs like
.uk,.ca, and.jpindicate sites associated with specific countries.
3. Uniqueness and Availability
- SL D: Each SL D within a specific TLD must be unique. So, while you can have multiple domains with the
example(likeexample.comandexample.org), each full domain name is unique. - TLD: TLDs are regulated and controlled by various organizations (like ICANN) and are not unique to a specific website. Many websites share the same TLD.
Example:
In the domain university.edu:
- SL D:
university(unique to this institution within.edu) - TLD:
.edu(indicating it is an educational institution)
In short, the SLD is the website’s specific identifier, while the TLD classifies or categorizes the domain at the highest level. Together, they create a unique domain name for each website on the internet.
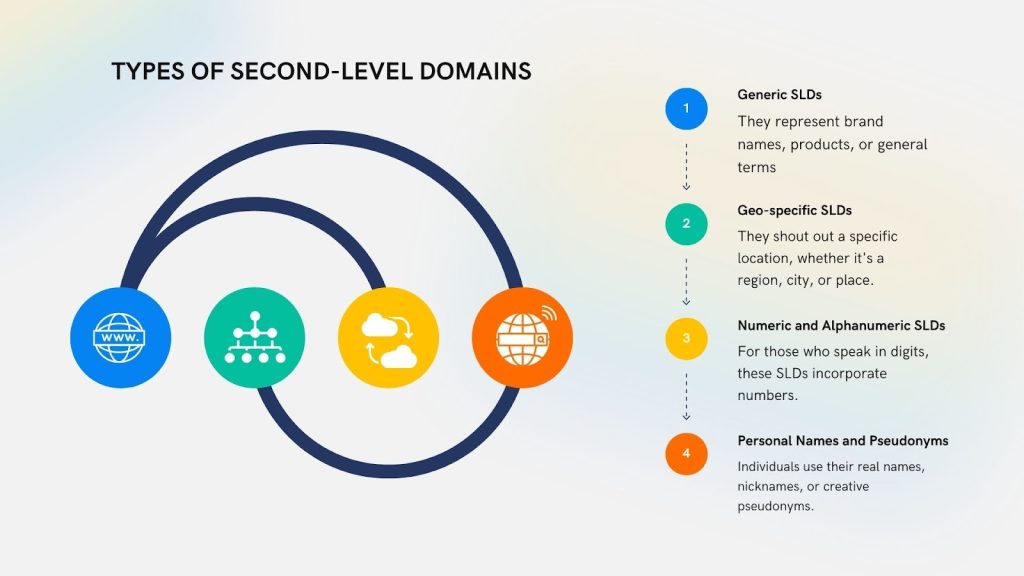
Uses of SLD
The Second-Level Domain is an essential component of a domain name, and it serves several key purposes. Here’s a look at its main uses:
1. Brand Identity and Recognition
- The SL D is often used to represent the name of a company, organization, or individual, making it a crucial part of the brand’s online identity.
- It allows users to instantly recognize and remember the site, which helps build brand trust and recall.
2. Uniqueness and Differentiation
- The SL D is unique within each Top-Level Domain (TLD), so it distinguishes one website from others.
- This uniqueness allows businesses and individuals to secure their own digital space, setting them apart from competitors.
3. Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- A relevant SL D that matches the brand name or keywords related to the business can improve search engine rankings.
- Search engines can associate the SL D with relevant keywords, potentially increasing the site’s visibility in search results.
4. Easy Navigation and Memorability
- A short, clear SL D makes the domain name easy to remember, type, and share, making it simpler for visitors to find the site directly.
- This is particularly useful for word-of-mouth marketing, as a memorable SL D encourages users to share the site with others.
5. Geographical or Industry-Specific Targeting
- Businesses or organizations can use location-based or industry-relevant terms in their S LDs, especially when paired with a specific TLD.
- For example,
londonflorist.ukcould indicate a florist in London, giving the business better visibility with local or industry-focused audiences.
6. Security and Credibility
- By using an S L D that matches the business name, organizations can assure users that the site is legitimate, reducing the risk of phishing or fake sites.
- A clear, professional S L D adds credibility, showing users that the site is trustworthy.
7. Flexibility for Subdomains
- The S L D serves as the main part of the domain, allowing flexibility to create subdomains for various purposes.
- For example, with the SL D
example.com, a business could create subdomains likeshop.example.comorblog.example.comfor different functions.
8. Legal Protection and Brand Safeguarding
- Registering an SL D that aligns with a trademark or brand name can offer some legal protection, preventing others from using similar domain names that could cause brand confusion.
In summary, the S L D is vital for branding, SEO, user experience, and security, making it one of the most strategic choices when establishing a web presence.